ROS 패키지 제작
ROS 패키지 설계
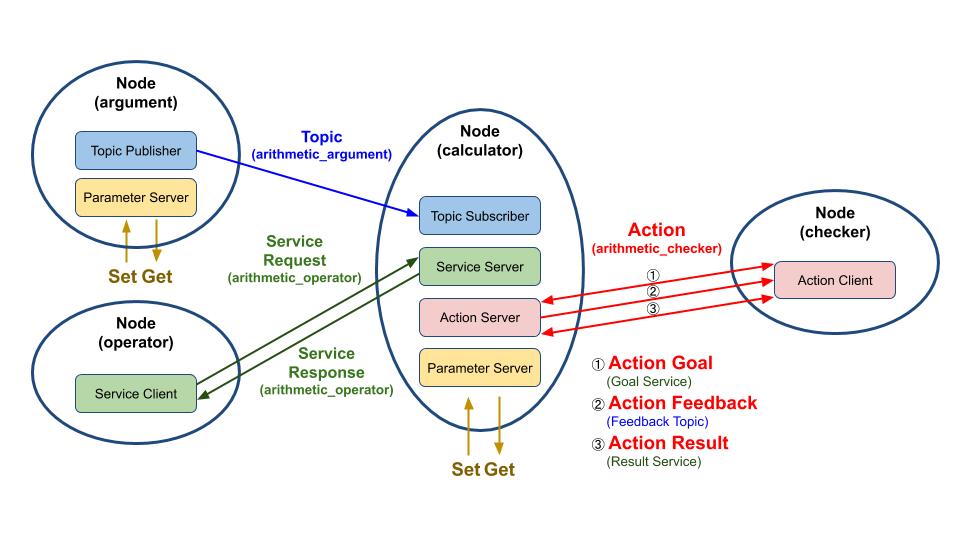
목적별로 나누어 노드 단위의 프로그램을 작성하고, 노드와 노드간의 데이터 통신을 설계해야 한다. 이번 예제 패키지는 토픽, 서비스, 액션으로 구성하고자 한다.
총 4개의 노드로 구성되며, 각 노드에서는 1개 이상의 토픽 퍼블리셔, 토픽 서브스크라이브, 서비스 서버, 서비스 클라이언트, 액션 서버, 액션 클라이언트가 존재한다. 중앙에 있는 노드는 다른 노드들과의 연동을 해야 하므로 가장 핵심적인 역할이다.
각각의 노드, 토픽, 서비스, 액션은 고유의 이름을 가지고 있다.
argument: arithmetic_argument 토픽 이름으로 현재 시간과 변수 a,b를 퍼블리시한다.operator: arithmetic_operator 서비스 이름으로 calculator 노드에게 연산자(+-*/)를 서비스 요청값으로 보낸다.calculator- 토픽이 생성된 시간과 변수 a,b를 arithmetic_argument 이름의 토픽을 서브스크라이브한다.
- 받은 변수 a,b와 operator 노드로부터 요청값으로 받은 연산자를 통해 계산하고(a 연산자 b), operator 노드에게 결괏값을 arithmetic_operator 이름으로 서비스 응답값을 보낸다.
- checker 노드로부터 액션 목표값(① action goal)을 받은 후부터 저장된 변수(a,b,연산자)를 가지고 연산한 값을 합한다. 그리고 연산이 끝난 계산식을 arithmetic_checker 이름으로 액션 피드백(② action feedback)을 checker 노드로 보낸다. 연산값의 합이 액션 목표값을 넘기면 최종 연산 합계를 arithmetic_checker 이름으로 액션 결괏값(③ action result)을 checker 노드로 보낸다.
checker: 연산값의 합계의 한계치를 arithmetic_checker 액션 이름으로 액션 목표값으로 전달한다.
ROS2 CPP 패키지 제작
ROS2 패키지 설정
🔥 주의 : 아래 파일들은 코드를 설명하기 위해서만 보고, 추후 git clone을 수행할 예정이므로 패키지를 직접 생성하지 않기를 바란다. 만약 패키지를 동일한 이름으로 생성할 경우 빌드에 문제가 생기므로, 다른 이름으로 생성하여 커스터마이징하거나, clone한 것을 사용하길 바란다.
- package.xml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<?xml-model href="http://download.ros.org/schema/package_format3.xsd" schematypens="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"?>
<!-- ROS2 패키지 설정파일의 package format이 세번째 버전이므로 3 -->
<package format="3">
<!-- 패키지 이름 -->
<name>topic_service_action_rclcpp_example</name>
<version>0.2.0</version>
<!-- 설명 -->
<description>ROS 2 rclcpp example package for the topic, service, action</description>
<maintainer email="jhyoon@todo.todo">jhyoon</maintainer>
<!-- 라이선스 -->
<license>Apache License 2.0</license>
<author email="passionvirus@gmail.com">Pyo</author>
<author email="routiful@gmail.com">Darby Lim</author>
<!-- 빌드툴 : ament_cmake -->
<buildtool_depend>ament_cmake</buildtool_depend>
<!-- dependency -->
<!-- ros2에서 사용하는 cpp툴 -->
<depend>rclcpp</depend>
<!-- cpp툴에서 action 사용하기 위함 -->
<depend>rclcpp_action</depend>
<!-- std 패키지 사용 -->
<depend>std_msgs</depend>
<!-- 토픽,서비스,액션 인터페이스 사용하는 패키지 -->
<depend>msg_srv_action_interface_example</depend>
<!-- 사용하고자 하는 Lint 패키지, 테스트 코드를 위한 의존성 패키지 -->
<test_depend>ament_lint_auto</test_depend>
<test_depend>ament_lint_common</test_depend>
<export>
<!-- build type : ament_cmake -->
<build_type>ament_cmake</build_type>
</export>
</package>
- CMakeLists.txt
CMakelist에는 크게 cmake 설정, 의존성 명시, 빌드, 설치, 테스트, ament package 매크로 설정으로 구성되어 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
# Set minimum required version of cmake, project name and compile options
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.5)
# project name
project(topic_service_action_rclcpp_example)
# C언어의 버전을 명시하지 않으면 C99를 기본으로 사용
if(NOT CMAKE_C_STANDARD)
set(CMAKE_C_STANDARD 99)
endif()
# C++의 버전을 명시하지 않으면 C++ 14를 기본으로 사용
if(NOT CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 14)
endif()
# GNU를 기본으로 사용하지만, Clang 컴파일러를 사용할 수도 있다.
if(CMAKE_COMPILER_IS_GNUCXX OR CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID MATCHES "Clang")
add_compile_options(-Wall -Wextra -Wpedantic)
endif()
# Find dependencies
# REQUIRED : 패키지를 찾고, 없으면 에러가 나도록 하는 옵션
find_package(ament_cmake REQUIRED)
find_package(rclcpp REQUIRED)
find_package(msg_srv_action_interface_example REQUIRED)
find_package(rclcpp_action REQUIRED)
# header 파일을 가져오기 위한 디렉토리
include_directories(include)
# Build
# 실제로 실행하는 파일 (node_name file_directory)
add_executable(argument src/arithmetic/argument.cpp)
# 프로그램 실행을 위해 필요한 의존성 패키지
ament_target_dependencies(argument
msg_srv_action_interface_example
rclcpp
)
add_executable(calculator src/calculator/main.cpp src/calculator/calculator.cpp)
# calculator에서는 action도 진행되기에 의존성 패키지에 추가
ament_target_dependencies(calculator
msg_srv_action_interface_example
rclcpp
rclcpp_action
)
add_executable(checker src/checker/main.cpp src/checker/checker.cpp)
ament_target_dependencies(checker
msg_srv_action_interface_example
rclcpp
rclcpp_action
)
add_executable(operator src/arithmetic/operator.cpp)
ament_target_dependencies(operator
msg_srv_action_interface_example
rclcpp
)
# Install
install(TARGETS
argument
calculator
checker
operator
DESTINATION lib/${PROJECT_NAME}
)
# 여기서 볼 수 있듯 launch 와 param은 share 폴더 아래에 저장해야 한다.
install(DIRECTORY launch param
DESTINATION share/${PROJECT_NAME}
)
# Test
# test시 필요한 의존성 패키지들, 추후 test시 colcon test 를 통해 사용 가능
# ament_lint_auto_find_test_dependenices를 통해 cpplint라는 코드 스타일을 점검해주는 패키지를 사용
if(BUILD_TESTING)
find_package(ament_lint_auto REQUIRED)
ament_lint_auto_find_test_dependencies()
endif()
# Macro for ament package
# ament 패키지를 위한 매크로 함수를 적어주어야 함
ament_package()
코드 다운로드 및 빌드
source ~/robot_ws/install/local_setup.bash는 ~/.bashrc에 없으면 추가하고, 있으면 추가하지 않아도 된다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
$ cd ~/robot_ws/src
$ git clone https://github.com/robotpilot/ros2-seminar-examples.git
$ cd ~/robot_ws && colcon build --symlink-install
Starting >>> msg_srv_action_interface_example
Starting >>> logging_rclpy_example
Finished <<< logging_rclpy_example [1.26s]
Starting >>> my_first_ros_rclcpp_pkg
Finished <<< my_first_ros_rclcpp_pkg [13.8s]
Starting >>> my_first_ros_rclpy_pkg
...
$ echo 'source ~/robot_ws/install/local_setup.bash' >> ~/.bashrc
$ source ~/.bashrc
$ . ~/robot_ws/install/local_setup.bash
. ~/robot_ws/install/local_setup.bash 를 하지 않으면 패키지를 찾지 못한다는 에러가 뜨니 주의하자.
빌드가 끝나고, 문제가 없다면 ~/robot_ws/install/topic_service_action_rclcpp_example 폴더 안에 우리가 작성한 ROS 인터페이스를 사용하기 위한 파일들이 저장될 것이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
$ ls ~/robot_ws/install
COLCON_IGNORE logging_rclpy_example rqt_example tf2_rclpy_example
local_setup.bash msg_srv_action_interface_example setup.bash time_rclcpp_example
local_setup.ps1 my_first_ros_rclcpp_pkg setup.ps1 time_rclpy_example
local_setup.sh my_first_ros_rclpy_pkg setup.sh topic_service_action_rclcpp_example
_local_setup_util_ps1.py rclcpp_tutorial setup.zsh topic_service_action_rclpy_example
_local_setup_util_sh.py rclpy_tutorial testbot_description
local_setup.zsh ros2env tf2_rclcpp_example
$ ls ~/robot_ws/install/topic_service_action_rclcpp_example/lib/topic_service_action_rclcpp_example/
argument calculator checker operator
$ ls ~/robot_ws/install/topic_service_action_rclcpp_example/share/topic_service_action_rclcpp_example/
cmake/ launch/ local_setup.sh package.dsv package.xml
environment/ local_setup.bash local_setup.zsh package.ps1 package.zsh
hook/ local_setup.dsv package.bash package.sh param/
이와 같이 argument, operator, calculator, checker와 같은 실행 스크립트가 생성되었다. 그리고 share 폴더 안에는 launch폴더와 param 폴더가 생성되었고, 각 폴더 안에는 arithmetic.launch.py와 arithmetic_config.yaml가 위치한다.
1
2
3
4
5
$ ls ~/robot_ws/install/topic_service_action_rclcpp_example/share/topic_service_action_rclcpp_example/launch/
arithmetic.launch.py
$ ls ~/robot_ws/install/topic_service_action_rclcpp_example/share/topic_service_action_rclcpp_example/param/
arithmetic_config.yaml
간단한 노드 실행
- calculator 노드 실행
이 노드는 토픽 서브스크라이버, 서비스 서버, 액션 서버 역할을 수행한다.
1
2
$ ros2 run topic_service_action_rclcpp_example calculator
[INFO]: Run calculator
실행했지만, 아직 받는 토픽이나 서비스, 액션이 없으므로 동작이 되지 않는다.
- argument 노드 실행
이 노드는 토픽 퍼블리셔 역할을 한다. 이를 실행하면 퍼블리시하고 있는 argument a, argument b가 표시될 것이고, 이를 통해 calculator 노드에서는 argument a, argument b와 함께 수신 받은 시간 정보가 출력될 것이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
$ ros2 run topic_service_action_rclcpp_example argument
[INFO]: Published argument_a 4.73
[INFO]: Published argument_b 7.43
[INFO]: Published argument_a 1.55
[INFO]: Published argument_b 6.38
[INFO]: Published argument_a 7.09
[INFO]: Published argument_b 5.89
[INFO]: Published argument_a 5.90
[INFO]: Published argument_b 8.21
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
ros2 run topic_service_action_rclcpp_example calculator
[INFO]: Run calculator
[INFO]: Timestamp of the message: sec 1658859718 nanosec 500974826
[INFO]: Subscribed argument a: 4.73
[INFO]: Subscribed argument b: 7.43
[INFO]: Timestamp of the message: sec 1658859719 nanosec 500985640
[INFO]: Subscribed argument a: 1.55
[INFO]: Subscribed argument b: 6.38
[INFO]: Timestamp of the message: sec 1658859720 nanosec 501005719
[INFO]: Subscribed argument a: 7.09
[INFO]: Subscribed argument b: 5.89
[INFO]: Timestamp of the message: sec 1658859721 nanosec 500910222
[INFO]: Subscribed argument a: 5.90
[INFO]: Subscribed argument b: 8.21
[INFO]: Timestamp of the message: sec 1658859722 nanosec 501017918
[INFO]: Subscribed argument a: 2.57
[INFO]: Subscribed argument b: 8.50
[INFO]: Timestamp of the message: sec 1658859723 nanosec 500904549
[INFO]: Subscribed argument a: 4.43
[INFO]: Subscribed argument b: 4.86
- operator 노드 실행
이 노드는 서비스 클라이언트 역할을 한다. calculator 노드에게 랜덤으로 선택한 연산자를 서비스 요청값으로 보내고, 연산된 결과값을 받아 터미널 창에 표시한다. 실제 계산식은 calculator 노드가 실행 중인 창에서 확인할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
$ ros2 run topic_service_action_rclcpp_example operator
[INFO]: Result 13.79
Press Enter for next service call.
[INFO]: Result 9.57
Press Enter for next service call.
[INFO]: Result 0.30
Press Enter for next service call.
[INFO]: Result 0.71
Press Enter for next service call.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
$ ros2 run topic_service_action_rclcpp_example calculator
[INFO]: 2.224688 + 7.350139 = 9.57483
[INFO]: 2.224688 / 7.350139 = 0.302673
[INFO]: Timestamp of the message: sec 1658859884 nanosec 500955814
[INFO]: Subscribed argument a: 5.25
[INFO]: Subscribed argument b: 7.38
[INFO]: 5.247090 / 7.383574 = 0.710644
[INFO]: 5.247090 / 7.383574 = 0.710644
Entor 키를 통해 서비스를 보낼 수 있다.
- checker 노드 실행
마지막으로 이 노드는 먼저 연산값의 합계 한계치를 액션 목표값으로 calculator 노드에 전달한다. 이후 checker 노드는 calculator 노드에게 액션 피드백을 받는데, 그 피드백은 각 연산과 그 결과의 string타입이다. 지정한 연산값의 합계가 목표 합계를 넘기면 checker 노드는 액션 결과값으로 calculator 노드로부터 최종 연산 합계를 전달받는다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
$ ros2 run topic_service_action_rclcpp_example checker
goal_total_sum : 50
[INFO]: Action goal accepted.
[INFO]: Action feedback:
[INFO]: 5.247090 / 7.383574 = 0.710644
[INFO]: Action feedback:
[INFO]: 5.247090 / 7.383574 = 0.710644
[INFO]: 5.247090 / 7.383574 = 0.710644
[INFO]: Action feedback:
[INFO]: 5.247090 / 7.383574 = 0.710644
[INFO]: 5.247090 / 7.383574 = 0.710644
[INFO]: 5.247090 / 7.383574 = 0.710644
[INFO]: Action feedback:
[INFO]: 5.247090 / 7.383574 = 0.710644
[INFO]: 5.247090 / 7.383574 = 0.710644
[INFO]: 5.247090 / 7.383574 = 0.710644
[INFO]: 5.247090 / 7.383574 = 0.710644
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
$ ros2 run topic_service_action_rclcpp_example calculator
[INFO]: 5.247090 / 7.383574 = 0.710644
[INFO]: 5.247090 / 7.383574 = 0.710644
[INFO]: 5.247090 / 7.383574 = 0.710644
[INFO]: 5.247090 / 7.383574 = 0.710644
[INFO]: 5.247090 / 7.383574 = 0.710644
[INFO]: 5.247090 / 7.383574 = 0.710644
[INFO]: 5.247090 / 7.383574 = 0.710644
[INFO]: 5.247090 / 7.383574 = 0.710644
[INFO]: 5.247090 / 7.383574 = 0.710644
동일한 logging이 출력되는데, 이는 목표 합계를 넘겼을 때, calculator 노드가 checker 노드에게 최종 연산 합계를 전달하기 때문이다. 합계의 한계치는 기본으로 50으로 설정되어 있다. 이를 수정하고자 한다면 checker 노드를 실행시킬 때 실행 인자로 -g 100 이라 입력하면 GOAL_TOTAL_SUM 이라는 합계 한계치 인자가 100으로 할당된다.
1
ros2 run topic_service_action_rclcpp_example checker -g 100
- launch 파일 실행
launch 파일을 통해 argument 노드와 calculator 노드를 한번에 실행시킬 수 있다. launch파일은 arithmetic.launch.py 파일이다.
1
ros2 launch topic_service_action_rclcpp_example arithmetic.launch.py
ROS 토픽 뜯어보기
이제는 위의 패키지에서 토픽에 대해 더 자세히 뜯어보고자 한다.
토픽은 비동기식 단방향 메시지 송수신 방식으로 메시지를 발행하는 퍼블리셔와 메시지를 구독하는 서브스크라이버 간의 통신이다. 이는 1:1 통신을 기본으로 하지만, 1:N, N:1, N:N도 가능하다.
위에서 토픽은 argument 노드에서 calculator 노드로의 argument a, argument b, 토픽을 생성한 시간에 대한 메시지 전달이다.

따라서 퍼블리셔와 서브스크라이버를 직접 작성해보고자 한다.
코드는 소스 파일과 헤더 파일이 존재하고, 각각 src 폴더와 include 폴더에 위치한다.
퍼블리셔
- topic_service_action_rclcpp_example/src/arithmetic/argument.cpp
- topic_service_action_rclcpp_example/include/arithmetic/argument.hpp
서브스크라이버
- topic_service_action_rclcpp_example/src/arithmetic/argument.cpp
- topic_service_action_rclcpp_example/include/arithmetic/argument.hpp
퍼블리셔
토픽 퍼블리셔 노드는 argument 노드이다.
- Node 설정
- QoS 설정
- create_publisher 설정 (timer 설정)
- 퍼블리시 함수 작성
- 헤더 파일
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
#ifndef ARITHMETIC__ARGUMENT_HPP_
#define ARITHMETIC__ARGUMENT_HPP_
// 시간을 다루는 라이브러리
#include <chrono>
// 동적 메모리를 다루는 라이브러리
#include <memory>
// 문자열을 다루는 라이브러리
#include <string>
// 서로다른 도메인을 다루는 라이브러리
#include <utility>
// rclcpp API를 담고 있는 rclcpp 헤더파일
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
// 만든 인터페이스를 담고 있는 헤더파일
#include "msg_srv_action_interface_example/msg/arithmetic_argument.hpp"
// rclcpp의 Node 클래스를 상속받는 Argument 클래스
class Argument : public rclcpp::Node
{
public:
using ArithmeticArgument = msg_srv_action_interface_example::msg::ArithmeticArgument;
// Argument 클래스의 생성자는 rclcpp의 NodeOptions를 인자로 받는다. NodeOptions에는 context, arguments, intra process communication, parameter, allocator와 같은 Node 생성을 위한 다양한 옵션이 존재
explicit Argument(const rclcpp::NodeOptions & node_options = rclcpp::NodeOptions());
virtual ~Argument();
private:
void publish_random_arithmetic_arguments();
void update_parameter();
// 토픽 메시지에 담을 랜덤 변수의 범위
float min_random_num_;
float max_random_num_;
// publisher와 timerbase 멤버변수가 선언되어 있다.
rclcpp::Publisher<ArithmeticArgument>::SharedPtr arithmetic_argument_publisher_;
rclcpp::TimerBase::SharedPtr timer_;
rclcpp::Subscription<rcl_interfaces::msg::ParameterEvent>::SharedPtr parameter_event_sub_;
rclcpp::AsyncParametersClient::SharedPtr parameters_client_;
};
#endif // ARITHMETIC__ARGUMENT_HPP_
- 소스 파일
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
// C언어 표준 인풋 아웃풋 라이브러리
#include <cstdio>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include <utility>
// 랜덤 숫자 생성 라이브러리
#include <random>
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
/// 프로그램 실행시 넘겨받은 인자를 다루는 ROS2 라이브러리
#include "rcutils/cmdline_parser.h"
// 위에서 생성한 argument 헤더 파일
#include "arithmetic/argument.hpp"
using namespace std::chrono_literals;
// Argument 클래스, 부모 클래스인 rclcpp:Node를 선언해주었는데, 첫번째 인자에는 노드 이름을, 두번째 인자에는 노드 옵션 변수를 명시한다.
Argument::Argument(const rclcpp::NodeOptions & node_options)
: Node("argument", node_options),
min_random_num_(0.0),
max_random_num_(0.0)
{
// QoS는 QoS 라이브러리를 이용하여 depth를 10으로 한다.
this->declare_parameter("qos_depth", 10);
int8_t qos_depth = this->get_parameter("qos_depth").get_value<int8_t>();
// 랜덤값 중 최소값로 0설정
this->declare_parameter("min_random_num", 0.0);
min_random_num_ = this->get_parameter("min_random_num").get_value<float>();
// 랜덤값 중 최대값로 9설정
this->declare_parameter("max_random_num", 9.0);
max_random_num_ = this->get_parameter("max_random_num").get_value<float>();
this->update_parameter();
/*
- History 옵션: KeepLast(depth : 10)
- Reliability 옵션: reliable
- Durability 옵션: volatile
*/
const auto QOS_RKL10V =
rclcpp::QoS(rclcpp::KeepLast(qos_depth)).reliable().durability_volatile();
// QoS는 publisher를 초기화할 때 두번째 인자로 들어가고, 첫번째 인자는 메시지 통신에 사용될 토픽명
arithmetic_argument_publisher_ =
this->create_publisher<ArithmeticArgument>("arithmetic_argument", QOS_RKL10V);
// 1초당 1번씩 publisher_random_arithmetic_arguments 멤버함수가 호출하도록 설정
timer_ =
this->create_wall_timer(1s, std::bind(&Argument::publish_random_arithmetic_arguments, this));
}
Argument::~Argument()
{
}
// timer에 의해 1초당 1번씩 호출
void Argument::publish_random_arithmetic_arguments()
{
std::random_device rd;
std::mt19937 gen(rd());
// ROS2 파라미터를 통해 얻은 숫자가 min(0) 과 max(9) 사이의 랜덤한 값으로 숫자를 생성
std::uniform_real_distribution<float> distribution(min_random_num_, max_random_num_);
// msg_srv_action_interface_example 패키지에 있는 msg 인터페이스를 선언
msg_srv_action_interface_example::msg::ArithmeticArgument msg;
// time-stamp
msg.stamp = this->now();
// argument a
msg.argument_a = distribution(gen);
// argument b
msg.argument_b = distribution(gen);
// 토픽 발행
arithmetic_argument_publisher_->publish(msg);
// logging
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Published argument_a %.2f", msg.argument_a);
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Published argument_b %.2f", msg.argument_b);
}
void Argument::update_parameter()
{
parameters_client_ = std::make_shared<rclcpp::AsyncParametersClient>(this);
while (!parameters_client_->wait_for_service(1s)) {
if (!rclcpp::ok()) {
RCLCPP_ERROR(this->get_logger(), "Interrupted while waiting for the service. Exiting.");
return;
}
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "service not available, waiting again...");
}
auto param_event_callback =
[this](const rcl_interfaces::msg::ParameterEvent::SharedPtr event) -> void
{
for (auto & changed_parameter : event->changed_parameters) {
if (changed_parameter.name == "min_random_num") {
auto value = rclcpp::Parameter::from_parameter_msg(changed_parameter).as_double();
min_random_num_ = value;
} else if (changed_parameter.name == "max_random_num") {
auto value = rclcpp::Parameter::from_parameter_msg(changed_parameter).as_double();
max_random_num_ = value;
}
}
};
parameter_event_sub_ = parameters_client_->on_parameter_event(param_event_callback);
}
// help
void print_help()
{
printf("For argument node:\n");
printf("node_name [-h]\n");
printf("Options:\n");
printf("\t-h Help : Print this help function.\n");
}
int main(int argc, char * argv[])
{
// cmdline_parser 라이브러리 함수를 사용하여, 만약 명령 인자에 -h 가 있을 경우 print_help 함수를 호출하고 종료
if (rcutils_cli_option_exist(argv, argv + argc, "-h")) {
print_help();
return 0;
}
// 초기화
rclcpp::init(argc, argv);
// Argument 클래스를 인스턴스화
auto argument = std::make_shared<Argument>();
// publish_random_arithmetic_arguments 실행
rclcpp::spin(argument);
// ctrl+c와 같은 시그널을 통해 노드 종료를 종료
rclcpp::shutdown();
return 0;
}
파라미터와 관련된 부분은 추후 다루도록 한다.
서브스크라이버
토픽 서브스크라이버 노드는 calculator 노드이다. calculator의 소스 코드는 토픽 서브스크라이버, 서비스 서버, 액션 서버를 모두 포함하고 있어서 매우 길어서 토픽 서브스크라이버와 관련된 부분만 살펴보도록 한다.
calculator 클래스는 토픽 퍼블리셔 노드와 마찬가지로 rclcpp::node를 상속하고, 생성자에서 calculator라는 노드 이름으로 초기화된다. 그리고 위에서와 동일하게 QoS를 생성한다.
서브스크라이버는 create_subscription을 통해 초기화되고, 해당 함수는 토픽명과 QoS, 콜백함수를 인자로 받는다. 첫번째, 두번째 인자는 Argument 클래스와 동일하게 넣고, 콜백함수는 std::bind가 아닌 람다 표현식을 사용했다. 콜백함수를 보면 인자를 통해 수신받은 메시지에 접근하여 멤버 변수에 저장한다.
- Node 설정
- QoS 설정
- create_subscription 설정
- 서브스크라이브 함수 작성
- 소스파일
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
// QoS 설정 - history : KeepLast, Reliability : reliable, Durability : volatile
const auto QOS_RKL10V =
rclcpp::QoS(rclcpp::KeepLast(qos_depth)).reliable().durability_volatile();
// 서브스크라이버 초기화, [토픽명, QoS]
arithmetic_argument_subscriber_ = this->create_subscription<ArithmeticArgument>(
"arithmetic_argument",
QOS_RKL10V,
[this](const ArithmeticArgument::SharedPtr msg) -> void
{
argument_a_ = msg->argument_a;
argument_b_ = msg->argument_b;
// logging - timestamp
RCLCPP_INFO(
this->get_logger(),
"Subscribed at: sec %ld nanosec %ld",
msg->stamp.sec,
msg->stamp.nanosec);
// logging - argument a, argument b
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Subscribed argument a : %.2f", argument_a_);
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Subscribed argument b : %.2f", argument_b_);
}
);
실행
실행하기 전에 CMakeLists.txt를 확인해서 add_executable 태그에 알맞게 들어가있는지 확인한다.
add_executable(argument src/arithmetic/argument.cpp)
add_executable(calculator src/calculator/main.cpp src/calculator/calculator.cpp)
첫번째 인자는 실행명, 그 다음 인자부터는 실행할 소스파일이다.
실행은 run과 launch 두가지 방식이 있다.
1
$ ros2 run topic_service_action_rclcpp_example calculator
1
$ ros2 run topic_service_action_rclcpp_example argument
1
$ ros2 launch topic_service_action_rclcpp_example arithmetic.launch.py
두 방법 모두 동작하는 것은 동일하다.
ROS2 python 패키지 제작
ROS2 패키지 설정
- package.xml (패키지 설정 파일)
topic_service_action_rclpy_example 패키지의 설정 파일은 다음과 같다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<?xml-model href="http://download.ros.org/schema/package_format3.xsd" schematypens="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"?>
<package format="3">
<name>topic_service_action_rclpy_example</name>
<version>0.2.0</version>
<description>ROS 2 rclpy example package for the topic, service, action</description>
<maintainer email="jhyoon@gmail.com">Pyo</maintainer>
<license>Apache License 2.0</license>
<author email="passionvirus@gmail.com">Pyo</author>
<author email="routiful@gmail.com">Darby Lim</author>
<!-- ros2에서 사용되는 python툴 -->
<depend>rclpy</depend>
<depend>std_msgs</depend>
<!-- 토픽, 서비스, 액션 인터페이스를 사용하기 위한 의존성 패키지 -->
<depend>msg_srv_action_interface_example</depend>
<test_depend>ament_copyright</test_depend>
<!-- python과 연동시키기 간편한 flake를 사용하기 위한 test 툴 -->
<test_depend>ament_flake8</test_depend>
<test_depend>ament_pep257</test_depend>
<!-- python에 사용될 test툴 -->
<test_depend>python3-pytest</test_depend>
<export>
<build_type>ament_python</build_type>
</export>
</package>
- setup.py (파이썬 패키지 설정 파일)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import glob
import os
from setuptools import find_packages
from setuptools import setup
package_name = 'topic_service_action_rclpy_example'
share_dir = 'share/' + package_name
setup(
name=package_name,
version='0.2.0',
packages=find_packages(exclude=['test']),
data_files=[
('share/ament_index/resource_index/packages', ['resource/' + package_name]),
(share_dir, ['package.xml']),
(share_dir + '/launch', glob.glob(os.path.join('launch', '*.launch.py'))),
(share_dir + '/param', glob.glob(os.path.join('param', '*.yaml'))),
],
install_requires=['setuptools'],
zip_safe=True,
author='Pyo, Darby Lim',
author_email='passionvirus@gmail.com, routiful@gmail.com',
maintainer='Pyo',
maintainer_email='passionvirus@gmail.com',
keywords=['ROS'],
classifiers=[
'Intended Audience :: Developers',
'License :: OSI Approved :: Apache Software License',
'Programming Language :: Python',
'Topic :: Software Development',
],
description='ROS 2 rclpy example package for the topic, service, action',
license='Apache License, Version 2.0',
tests_require=['pytest'],
entry_points={
'console_scripts': [
'argument = topic_service_action_rclpy_example.arithmetic.argument:main',
'operator = topic_service_action_rclpy_example.arithmetic.operator:main',
'calculator = topic_service_action_rclpy_example.calculator.main:main',
'checker = topic_service_action_rclpy_example.checker.main:main',
],
},
)
살펴볼 부분은 data_files와 entry_points 이다.
data_files
- 이 패키지에서 사용되는 파일들을 기입하여 함께 배포한다. 주로 resource 폴더 내에 있는 ament_index를 위한 패키지의 이름의 빈 파일이나, package.xml, .launch.py, .yaml 등을 기입한다. 이를 통해 빌드 후 해당 파일들이 설치 폴더에 추가된다.
- 이 패키지에서는
arithmetic.launch.py런치 파일과arithmetic_config.yaml파라미터 파일이 사용되므로 아래와 같이 해당 파일들의 설정을 추가한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
data_files=[
('share/ament_index/resource_index/packages', ['resource/' + package_name]),
(share_dir, ['package.xml']),
(share_dir + '/launch', glob.glob(os.path.join('launch', '*.launch.py'))),
(share_dir + '/param', glob.glob(os.path.join('param', '*.yaml'))),
],
entry_points
- entry_points는 설치하여 사용할 실행 가능한 콘솔 스크립트 이름과 호출 함수를 기입한다.
ros2 run과 같은 노드 실행 명령어를 통해 각 노드를 실행할 것이므로 entry_points에 추가한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
entry_points={
'console_scripts': [
'argument = topic_service_action_rclpy_example.arithmetic.argument:main',
'operator = topic_service_action_rclpy_example.arithmetic.operator:main',
'calculator = topic_service_action_rclpy_example.calculator.main:main',
'checker = topic_service_action_rclpy_example.checker.main:main',
],
},
코드 다운로드 및 빌드
위의 git 클론을 하게 되면, rclcpp 뿐만 아니라 rclpy 패키지도 함께 들어있다.
~/robot_ws/install/topic_service_action_rclpy_example 폴더가 존재하는지 확인한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
~/robot_ws/install$ ls
COLCON_IGNORE logging_rclpy_example rqt_example tf2_rclpy_example
local_setup.bash msg_srv_action_interface_example setup.bash time_rclcpp_example
local_setup.ps1 my_first_ros_rclcpp_pkg setup.ps1 time_rclpy_example
local_setup.sh my_first_ros_rclpy_pkg setup.sh topic_service_action_rclcpp_example
_local_setup_util_ps1.py rclcpp_tutorial setup.zsh topic_service_action_rclpy_example
_local_setup_util_sh.py rclpy_tutorial testbot_description
local_setup.zsh ros2env tf2_rclcpp_example
간단한 노드 실행
- calculator 노드 실행
아직 주고 받는 토픽, 서비스, 액션이 없으니 대기 상태이다.
1
$ ros2 run topic_service_action_rclpy_example calculator
- argument 노드 실행
토픽 퍼블리셔 역할을 하는 노드이다. 실행하고 나면 퍼블리시하고 있는 argument a, argument b가 표시된다. 그리고, calculator 노드를 실행시킨 터미널에서도 토픽을 수신받은 시간에 대한 정보와 argument a, argument b가 표시된다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
$ ros2 run topic_service_action_rclpy_example argument
[INFO]: Published argument a: 4.0
[INFO]: Published argument b: 5.0
[INFO]: Published argument a: 1.0
[INFO]: Published argument b: 9.0
[INFO]: Published argument a: 0.0
...
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
$ ros2 run topic_service_action_rclpy_example calculator
[INFO]: Timestamp of the message: builtin_interfaces.msg.Time(sec=1659430104, nanosec=525228141)
[INFO]: Subscribed argument a: 4.0
[INFO]: Subscribed argument b: 5.0
[INFO]: Timestamp of the message: builtin_interfaces.msg.Time(sec=1659430105, nanosec=525153321)
[INFO]: Subscribed argument a: 1.0
[INFO]: Subscribed argument b: 9.0
[INFO]: Timestamp of the message: builtin_interfaces.msg.Time(sec=1659430106, nanosec=525057834)
[INFO]: Subscribed argument a: 0.0
[INFO]: Subscribed argument b: 1.0
...
- operator 노드 실행
서비스 클라이언트 역할을 하는 노드를 실행해보자. 그러면 calculator 노드에게 랜덤으로 선택한 연산자를 서비스 요청값으로 보내고, 연산된 결과값을 반환받아 터미널에 표시한다. 실제 계산식은 calculator 노드가 실행 중인 창에서 확인할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
$ ros2 run topic_service_action_rclpy_example operator
[INFO]: Result: 3.0
Press Enter for next service call.
[INFO]: Result: 14.0
Press Enter for next service call.
[INFO]: Result: 0.6666666865348816
Press Enter for next service call.
...
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
$ ros2 run topic_service_action_rclpy_example calculator
[INFO]: Timestamp of the message: builtin_interfaces.msg.Time(sec=1659430234, nanosec=525041106)
[INFO]: Subscribed argument a: 6.0
[INFO]: Subscribed argument b: 2.0
[INFO]: 6.0 / 2.0 = 3.0
[INFO]: Timestamp of the message: builtin_interfaces.msg.Time(sec=1659430238, nanosec=525190661)
[INFO]: Subscribed argument a: 2.0
[INFO]: Subscribed argument b: 7.0
[INFO]: 2.0 * 7.0 = 14.0
[INFO]: Timestamp of the message: builtin_interfaces.msg.Time(sec=1659430240, nanosec=525128381)
[INFO]: Subscribed argument a: 2.0
[INFO]: Subscribed argument b: 3.0
[INFO]: 2.0 / 3.0 = 0.6666666666666666
- checker 노드 실행
마지막으로 checker 노드는 연산값의 합계의 한계치를 액션 목표값으로 전달하고, calculator 노드는 이를 받은 후부터의 연산값을 합하여 액션 피드백으로 각 연산 계산식을 보낸다. 지정한 목표 합계를 넘기면 액션 결과값으로 최종 연산 합계를 보낸다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
$ ros2 run topic_service_action_rclpy_example checker
[INFO]: Action goal accepted.
[INFO]: Action feedback: ['9.0 + 8.0 = 17.0']
[INFO]: Action feedback: ['9.0 + 8.0 = 17.0', '9.0 + 8.0 = 17.0']
[INFO]: Action feedback: ['9.0 + 8.0 = 17.0', '9.0 + 8.0 = 17.0', '9.0 + 8.0 = 17.0']
[INFO]: Action succeeded!
[INFO]: Action result(all formula): ['9.0 + 8.0 = 17.0', '9.0 + 8.0 = 17.0', '9.0 + 8.0 = 17.0']
[INFO]: Action result(total sum): 51.0
합계 한계치는 기본적으로 50으로 지정되어 있고, 이를 수정하려면 checker 노드 실행할 때 -g 인자를 통해 직접 할당할 수 있다.
1
ros2 run topic_service_action_rclpy_example checker -g 100
- launch 파일 실행
argument 노드와 calculator 노드를 한번에 실행시키고자 한다면 launch파일을 실행하면 된다.
1
ros2 launch topic_service_action_rclpy_example arithmetic.launch.py
ROS2 토픽 뜯어보기
동일하게 토픽에 대해 자세하게 뜯어볼 것이다.
퍼블리셔
- topic_service_action_rclpy_example/topic_service/action_rclpy_example/arithmetic/argument.py
서브스크라이버
- topic_service_action_rclpy_example/topic_service/action_rclpy_example/calculator/calculator.py
퍼블리셔
토픽 퍼블리셔 역할을 하는 argument 노드이다.
- Node 설정
- QoS 설정
- create_publisher 설정
- 퍼블리시 함수 작성
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
import random
from msg_srv_action_interface_example.msg import ArithmeticArgument
from rcl_interfaces.msg import SetParametersResult
# ros2에서 사용하는 python 모듈
import rclpy
# 노드
from rclpy.node import Node
# 파라미터
from rclpy.parameter import Parameter
# QoS 패키지
from rclpy.qos import QoSDurabilityPolicy
from rclpy.qos import QoSHistoryPolicy
from rclpy.qos import QoSProfile
from rclpy.qos import QoSReliabilityPolicy
# rclpy.node 모듈의 Node 클래스를 상속한다.
class Argument(Node):
def __init__(self):
# 생성자 - argument 노드 이름으로 초기화
super().__init__('argument')
# 파라미터 설정
self.declare_parameter('qos_depth', 10)
qos_depth = self.get_parameter('qos_depth').value
self.declare_parameter('min_random_num', 0)
self.min_random_num = self.get_parameter('min_random_num').value
self.declare_parameter('max_random_num', 9)
self.max_random_num = self.get_parameter('max_random_num').value
self.add_on_set_parameters_callback(self.update_parameter)
# QoS 설정
### RELIABLE : 데이터 수신에 집중, 유실 시 재전송 <-> BEST_EFFORT : 데이터 송신에 집중, 전송 속도 중시
### KEEP_LAST : 정해진 메시지 큐 사이즈(depth)만큼 데이터를 보관 <-> KEEP_ALL : 모든 데이터를 보관
### VOLATILE : 서브스크라이버 생성되기 전의 데이터는 삭제 <-> TRANSIENT_LOCAL : 서브스크라이버 생성되기 전의 데이터도 보관
QOS_RKL10V = QoSProfile(
reliability=QoSReliabilityPolicy.RELIABLE,
history=QoSHistoryPolicy.KEEP_LAST,
depth=qos_depth,
durability=QoSDurabilityPolicy.VOLATILE)
# 퍼블리셔 선언, (토픽 타입, 이름, QoS 설정)
self.arithmetic_argument_publisher = self.create_publisher(
ArithmeticArgument,
'arithmetic_argument',
QOS_RKL10V)
# 함수 실행 주기, 1초에 1번 실행하도록 설정
# 이전 설정은 모두 퍼블리시를 위한 설정이고, publish_random_arithmetic_argments가 실제 토픽 발행 부분
self.timer = self.create_timer(1.0, self.publish_random_arithmetic_arguments)
# 메시지 타입은 arithmeticArgument, timestamp, 랜덤의 argument a,b 저장
def publish_random_arithmetic_arguments(self):
msg = ArithmeticArgument()
# timestamp 지정
msg.stamp = self.get_clock().now().to_msg()
# 랜덤의 argument a 지정
msg.argument_a = float(random.randint(self.min_random_num, self.max_random_num))
# 랜덤의 argument b 지정
msg.argument_b = float(random.randint(self.min_random_num, self.max_random_num))
# 토픽 발행
self.arithmetic_argument_publisher.publish(msg)
# logging
self.get_logger().info('Published argument a: {0}'.format(msg.argument_a))
self.get_logger().info('Published argument b: {0}'.format(msg.argument_b))
def update_parameter(self, params):
for param in params:
if param.name == 'min_random_num' and param.type_ == Parameter.Type.INTEGER:
self.min_random_num = param.value
elif param.name == 'max_random_num' and param.type_ == Parameter.Type.INTEGER:
self.max_random_num = param.value
return SetParametersResult(successful=True)
def main(args=None):
rclpy.init(args=args)
try:
argument = Argument()
# 1초에 1번씩 함수 실행
try:
rclpy.spin(argument)
# Ctrl+C와 같은 시그널이 들어오면 종료
except KeyboardInterrupt:
argument.get_logger().info('Keyboard Interrupt (SIGINT)')
finally:
argument.destroy_node()
finally:
rclpy.shutdown()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
서브스크라이버
토픽 서브스크라이버 역할을 하는 calculator 노드이다. calculator의 소스 코드는 토픽 서브스크라이버, 서비스 서버, 액션 서버를 모두 포함하고 있어서 매우 길어서 토픽 서브스크라이버와 관련된 부분만 살펴보도록 한다.
calculator 클래스는 rclpy.node 모듈의 Node 클래스를 상속하고 있으며, 생성자에서 calculator 라는 노드 이름으로 초기화된다. 그 뒤에는 QoSProfile 클래스를 사용하여 서브스크라이버의 QoS 설정을 해준다.
- Node 설정
- QoS 설정
- create_subscription 설정
- 서브스크라이브 함수 작성
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
import rclpy
from rclpy.executors import MultiThreadedExecutor
# Node 클래스를 상속
class Calculator(Node):
def __init__(self):
# calculator 이름으로 초기화
super().__init__('calculator')
# 변수 초기화
self.argument_a = 0.0
self.argument_b = 0.0
self.callback_group = ReentrantCallbackGroup()
(일부 코드 생략)
# QoS 설정
QOS_RKL10V = QoSProfile(
reliability=QoSReliabilityPolicy.RELIABLE,
history=QoSHistoryPolicy.KEEP_LAST,
depth=qos_depth,
durability=QoSDurabilityPolicy.VOLATILE)
# 서브스크라이버 설정
### 퍼블리셔와 동일하게 (토픽 타입(ArithmeticArgument), 토픽 이름, QoS 설정) + callback함수
### get_arithmetic_argument : 퍼블리셔로부터 메시지를 서브스크라이브할 때마다 실행되는 함수
### callback_group = ReentrantCallbackGroup : 콜백함수를 병렬로 실행할 수 있게 해주는 multithread 기능이 있다. 지정해주지 않아도 되는데, 지정하지 않으면 MultuallyExclusiveCallbackGroup이 기본으로 설정된다. 이는 한번에 하나의 콜백함수만을 실행하도록 허용하는 것이고, ReenttrantCallbackGroup은 제한없이 콜백함수를 병렬로 실행시켜준다. callback_group 설정으로는 create_subscription(), create_service(), ActionServer(), create_timer() 에서 사용된다.
self.arithmetic_argument_subscriber = self.create_subscription(
ArithmeticArgument,
'arithmetic_argument',
self.get_arithmetic_argument,
QOS_RKL10V,
callback_group=self.callback_group)
# callback 함수 : ArithmeticArgument 타입의 메시지의 arithmetic_argument라는 토픽을 서브스크라이브 하면 실행된다.
def get_arithmetic_argument(self, msg):
# 서브스크라이브한 msg의 argument a와 b를 멤버 변수에 저장
self.argument_a = msg.argument_a
self.argument_b = msg.argument_b
# logging
self.get_logger().info('Subscribed at: {0}'.format(msg.stamp))
self.get_logger().info('Subscribed argument a: {0}'.format(self.argument_a))
self.get_logger().info('Subscribed argument b: {0}'.format(self.argument_b))
def main(args=None):
rclpy.init(args=args)
try:
calculator = Calculator()
# multithreadExecutor가 있는데, 이는 스레드 풀(thread pool)을 사용하여 콜백을 실행하는 것인데, num_threads로 스레드 수를 지정할 수 있고, 지정하지 않을 경우 multiprocessing.cpu_count()를 통해 시스템에서 가용할 수 있는 스레드 수를 지정받는다. 둘다 해당되지 않으면 단일 스레드를 사용한다. excutor는 콜백이 병렬로 발생하도록 허용하여 ReentrantCallbackGroup과 함께 사용하여 콜백함수를 병렬로 실행할 수 있게 한다.
executor = MultiThreadedExecutor(num_threads=4)
# 위에서 설정한 executor를 calculator 노드에 추가
executor.add_node(calculator)
try:
executor.spin()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
calculator.get_logger().info('Keyboard Interrupt (SIGINT)')
finally:
executor.shutdown()
calculator.arithmetic_action_server.destroy()
calculator.destroy_node()
finally:
rclpy.shutdown()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
실행
실행하기 전에 setup.py를 다시 한 번 점검하자.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
entry_points={
'console_scripts': [
'argument = topic_service_action_rclpy_example.arithmetic.argument:main',
'operator = topic_service_action_rclpy_example.arithmetic.operator:main',
'calculator = topic_service_action_rclpy_example.calculator.main:main',
'checker = topic_service_action_rclpy_example.checker.main:main',
],
},
entry_points에 argument.py의 main함수 실행와 calculator.py의 main함수 실행하는 부분이 담겨져 있어야 한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
$ ros2 launch topic_service_action_rclcpp_example arithmetic.launch.py
[INFO] [launch]: All log files can be found below /home/jhyoon/.ros/log/2022-08-02-18-33-29-121351-LAPTOP-FCNUC3SV-442
[INFO] [launch]: Default logging verbosity is set to INFO
[INFO] [argument-1]: process started with pid [444]
[INFO] [calculator-2]: process started with pid [446]
[calculator-2] [INFO]: Run calculator
[argument-1] [INFO]: Published argument_a 7.62
[argument-1] [INFO]: Published argument_b 1.43
[calculator-2] [INFO]: Timestamp of the message: sec 1659432810 nanosec 256482232
[calculator-2] [INFO]: Subscribed argument a: 7.62
[calculator-2] [INFO]: Subscribed argument b: 1.43
[argument-1] [INFO]: Published argument_a 8.76
[argument-1] [INFO]: Published argument_b 0.60
[calculator-2] [INFO]: Timestamp of the message: sec 1659432811 nanosec 256391424
[calculator-2] [INFO]: Subscribed argument a: 8.76
[calculator-2] [INFO]: Subscribed argument b: 0.60
